Terpineol in the Chemical Industry: Properties and Applications
Terpineol is a naturally occurring monoterpene alcohol found in essential oils of various plants, such as pine and eucalyptus. It exists in three isomeric forms: alpha-, beta-, and gamma-terpineol, with alpha-terpineol being the most commercially important. Terpineol has a pleasant lilac or pine odor, making it a common fragrance and flavoring agent in perfumes, cosmetics, and food products.
In the chemical industry, terpineol is valued for its versatile applications beyond its aromatic properties. It serves as a solvent in resins, gums, and varnishes, as well as in the production of pharmaceuticals and disinfectants. Its role as an emulsifier and stabilizer in chemical processes further underscores its industrial relevance. Additionally, terpineol is used in the flotation process for ore extraction, particularly in separating non-ferrous metals.
Understanding terpineol’s chemical properties, such as its moderate volatility, good solvency, and low toxicity, is crucial for optimizing its industrial uses. Its ability to dissolve hydrophobic compounds and mix them with various solvents makes it a valuable additive in formulations requiring solubility control and product stability. Its low environmental impact and biodegradability also align with the growing demand for greener chemicals in industrial applications.
Chemical Properties of Terpineol
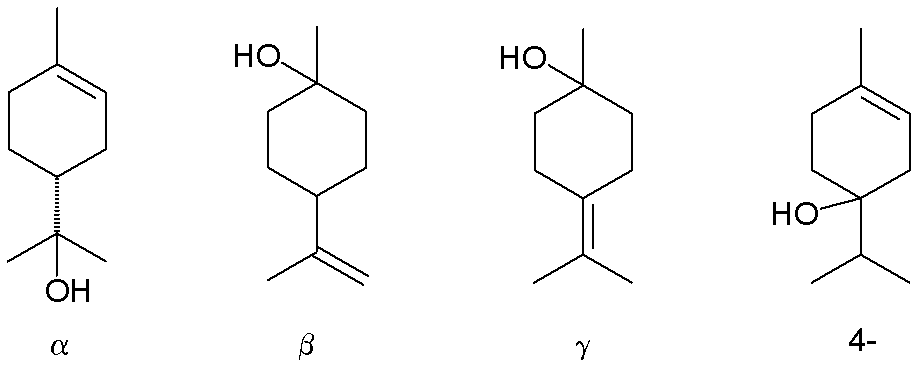
Terpineol (C₁₀H₁₈O) is a monoterpene alcohol with three isomeric forms: alpha-, beta-, and gamma-terpineol. These isomers differ in the arrangement of the hydroxyl group (-OH) and the double bonds within the carbon chain, affecting their physical properties and odor profiles. Alpha-terpineol is the most commercially significant, known for its lilac or pine-like fragrance. Beta- and gamma-terpineol are less prominent but share similar uses in fragrances and solvents.
Structurally, terpineol’s molecular formula consists of 10 carbon atoms, 18 hydrogen atoms, and 1 oxygen atom. It features a six-membered ring (cyclohexane) with a hydroxyl group attached, making it an alcohol.
Physical properties:
● Boiling point: 214°C (alpha-terpineol)
● Solubility: Sparingly soluble in water, highly soluble in organic solvents like ethanol and diethyl ether.
● Density: Around 0.93 g/cm³ at 20°C
Terpineol is naturally extracted from pine oil, where it is present as a major component. The extraction process involves steam distillation, followed by fractional distillation to isolate the terpineol isomers. However, it can also be produced synthetically from turpentine oil, which is derived from the resin of pine trees. The synthetic production of terpineol often involves the hydration of terpene hydrocarbons like alpha-pinene.
This compound’s versatility and pleasant aroma make it valuable in cosmetics, fragrances, and as a solvent in chemical industries.
Industrial Applications of Terpineol
Terpineol is widely utilized in perfumes, soaps, and cosmetics due to its distinctive lilac scent, which is pleasant, floral, and reminiscent of pine. This aroma makes alpha-terpineol, in particular, a valuable ingredient in creating fragrances for perfumes and personal care products. It enhances the olfactory appeal of products such as lotions, shampoos, and soaps, giving them a natural, long-lasting scent that consumers favor. In addition to its scent, terpineol’s relatively low toxicity and natural origin from essential oils make it a favored ingredient in natural and organic cosmetic formulations.
In the chemical industry, terpineol plays a crucial role as a solvent in resins, paints, and coatings. Its ability to dissolve both polar and non-polar compounds makes it effective in formulations that require uniform dispersion of various components. In paints and coatings, terpineol enhances flow properties and aids in the drying process without compromising the finish or durability. Similarly, resins help in dissolving polymers, leading to improved viscosity and workability of materials in adhesives, varnishes, and sealants.
In industrial cleaners and disinfectants, terpineol’s solvency and antimicrobial properties make it a powerful cleaning agent. It is effective at breaking down grease, oils, and other stubborn substances, making it suitable for use in degreasers, household cleaners, and surface disinfectants. Its natural origin and biodegradability also align with the industry’s increasing focus on safer, eco-friendly cleaning solutions.
Terpineol also finds use in topical applications and medicinal formulations. Due to its anti-inflammatory and antiseptic properties, it is used in ointments, creams, and lotions that target skin irritation, cuts, and burns. Terpineol’s soothing scent further enhances the sensory experience in personal care and medicinal products, making it an ideal additive in balms and rubs designed to relieve respiratory conditions, such as in vapor rubs or chest ointments.
One of terpineol’s technical advantages is its role as an emulsifier in various chemical processes. It aids in stabilizing mixtures of water and oil, making it valuable in the production of creams, lotions, and other emulsified products where uniform consistency is key. In industrial formulations, it ensures that ingredients stay mixed during storage and application, reducing the risk of separation. This property makes terpineol essential in both consumer and industrial products that require stable, homogenous formulations.
Overall, terpineol’s multifaceted nature as a fragrance, solvent, cleaner, and emulsifier demonstrates its importance in a wide range of industries, from cosmetics to heavy-duty industrial applications.
















